Variational polarimetric radar algorithm for retrieving the
properties of rain and hail
From this page you can obtain the code and some test data for a
variational algorithm for estimating rain rate and hail intensity from
polarimetric radar measurements. Variational retrieval methods involve
finding the optimal distribution of variables (e.g. rain rate and mean
drop size) that best "forward-model" the observations in a least
squares sense. This is particularly useful for the problem of
retrieving rain and hail properties from polarimetric measurements of
Z, Zdr and Phidp, which provide complementary
information yet may be affected by noise. The details of the
algorithm are provided in the paper below.
The algorithm has so far been tested on data from the S-band radar
(3 GHz) at Chilbolton. This frequency is only weakly affected by
attenuation, which makes the retrieval problem easier. An obvious
question is whether the algorithm can be applied to higher
frequencies, such as C-band (5.6 GHz) or X-band (10 GHz). The answer
is "yes" in principle, but probably not without some clever use of
constraints and possibly modification to the state variables that are
used.
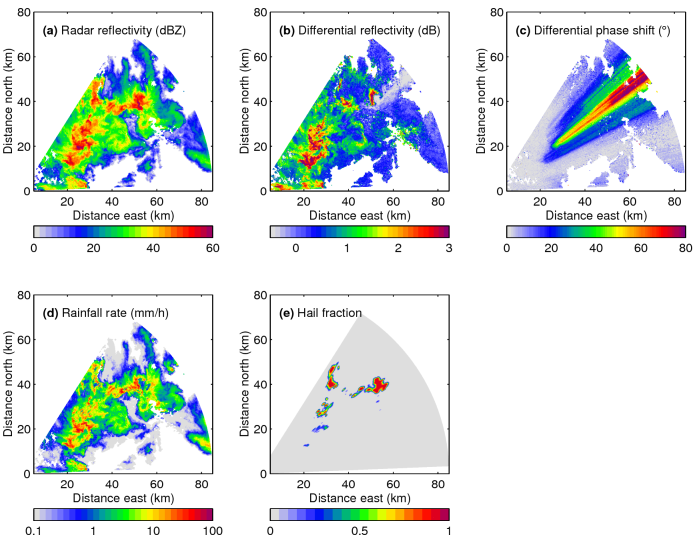
To illustrate the input and output of the algorithm, the top three
panels of the figure below show the input fields (radar reflectivity
as with a conventional radar, plus two fields from the polarization
capability), while the bottom two show the retrieved rain rate and the
location of the hail shafts.
Paper
- Hogan, R. J., 2007: A variational scheme for retrieving rainfall
rate and hail reflectivity fraction from polarization
radar. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatology, 46, 1544-1564: PDF file
Presentation
- Talk at Department of Meteorology, Reading, January 2008: PPT
file
Source code
If you use the code and have any comments, queries, requests or
bug-fixes then please contact Robin Hogan. I'm also
interested to know of any uses of the code - then I can also keep you
updated on changes, bug-fixes etc.

|